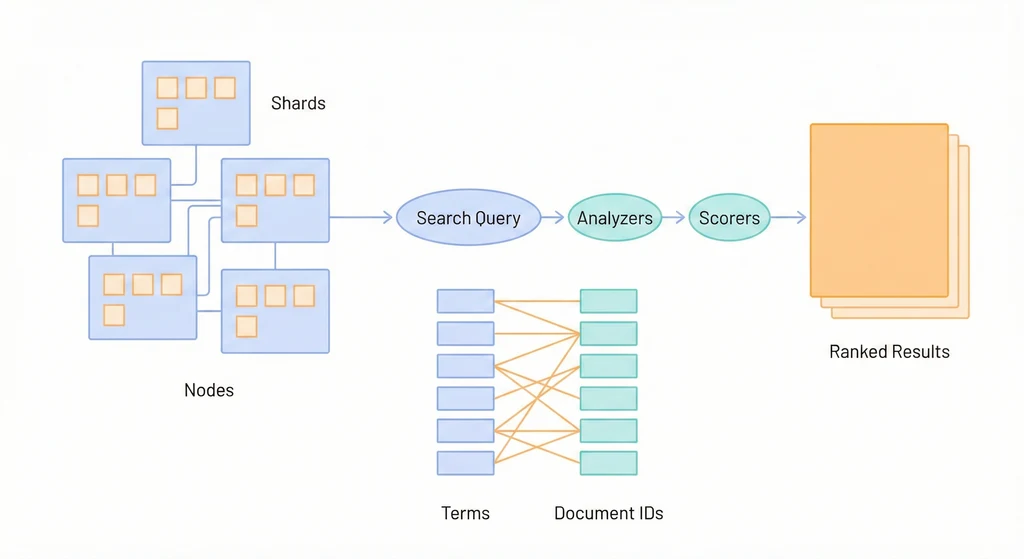
Elasticsearch 深入:當 PostgreSQL FTS 不夠用
Log Management 介紹了用 EFK/ELK Stack 收集和搜尋日誌。但 Elasticsearch 不只是日誌搜尋引擎——它是一個通用的分散式搜尋與分析引擎。當你的應用需要複雜的全文搜尋、分面過濾、自動補全、模糊匹配,而 PostgreSQL 的 Full-Text Search 開始顯得力不從心時,就是考慮引入 Elasticsearch 的時機。
這篇文章聚焦在 Elasticsearch 作為應用搜尋引擎的角色:怎麼設計 Mapping、怎麼寫好的查詢、怎麼調校效能。和日誌用途不同,應用搜尋對 relevance(搜尋結果相關性)和 latency(回應時間)有更高的要求。
架構概覽
flowchart TD App["應用程式"] -->|Index 寫入| Coord["Coordinator Node\n路由請求"] App -->|Search 查詢| Coord Coord --> N1["Data Node 1"] Coord --> N2["Data Node 2"] Coord --> N3["Data Node 3"] subgraph Index["Index: products"] S0["Shard 0\nPrimary"] --> R0["Shard 0\nReplica"] S1["Shard 1\nPrimary"] --> R1["Shard 1\nReplica"] S2["Shard 2\nPrimary"] --> R2["Shard 2\nReplica"] end N1 --- S0 N2 --- S1 N3 --- S2 N1 --- R1 N2 --- R2 N3 --- R0
什麼時候需要 Elasticsearch
PostgreSQL 進階 涵蓋了 PostgreSQL 的 Full-Text Search(tsvector、tsquery、ts_rank)。對很多應用來說,PostgreSQL FTS 已經夠用了——不需要額外部署和維護一套搜尋基礎設施。但以下場景會讓 PostgreSQL FTS 開始吃力:
-
模糊搜尋 / 容錯:使用者輸入
elasticserch(拼錯),PostgreSQL FTS 找不到任何結果。Elasticsearch 的fuzziness參數可以自動處理 1-2 個字元的拼寫錯誤,還是能找到elasticsearch相關的文件。 -
複雜分面搜尋(Faceted Search):電商網站的左側篩選欄——按品牌、價格區間、顏色、評分過濾,同時顯示每個篩選條件的數量。PostgreSQL 要寫很多
COUNT(*) ... GROUP BY子查詢,效能隨篩選條件增加急劇下降。Elasticsearch 的 Aggregation 天生就是為這個設計的。 -
多語言自動偵測:你的平台有中文、英文、日文內容。PostgreSQL 的 FTS 需要在建立
tsvector時指定語言配置,無法自動偵測。Elasticsearch 可以對同一個欄位套用多個 Analyzer,甚至用 language detection plugin 自動選擇。 -
大量文件(10M+):PostgreSQL FTS 在百萬級文件的全文搜尋已經需要仔細調校 GIN index,千萬級以上效能明顯下滑。Elasticsearch 天生分散式,可以水平擴展到數十個節點,輕鬆處理數十億文件。
-
高吞吐量的即時索引:每秒數千筆資料的即時索引需求(例如社群平台的貼文、即時庫存更新),PostgreSQL 的單一寫入節點會成為瓶頸。
-
複雜的相關性調校:搜尋結果的排序不只是「包含關鍵字」——需要考慮欄位權重、新鮮度、熱門度、使用者偏好。Elasticsearch 的
function_score提供極大的彈性。
總結:如果搜尋只是你應用的一個小功能(「在我的 app 裡搜尋」),用 PostgreSQL FTS。如果搜尋就是你的核心功能(「搜尋就是我的 app」),用 Elasticsearch。
核心概念
在深入 Mapping 和查詢之前,先釐清 Elasticsearch 的基本概念。如果你來自關聯式資料庫的背景,這些對照會有幫助,但要注意它們不是完全等價的。
Index, Document, Field
| Elasticsearch | 對應的 RDBMS 概念 | 說明 |
|---|---|---|
| Index | Table | 一組具有相同結構的文件集合 |
| Document | Row | 一筆資料,JSON 格式 |
| Field | Column | 文件中的一個欄位 |
| Mapping | Schema | 欄位的型態與分析方式 |
看起來很像資料庫?但 Elasticsearch 不是資料庫。關鍵差異:
- 沒有 Transaction:不支援 ACID。寫入後不保證立即可搜尋(有 1 秒的 refresh interval)。
- Eventually Consistent:Replica 同步有延遲。讀到舊資料是正常的。
- 不適合作為 Primary Data Store:Elasticsearch 不應該是資料的唯一來源。你的「真相」應該在 PostgreSQL 或其他 ACID 資料庫裡,Elasticsearch 是搜尋用的副本。
Shard & Replica
Elasticsearch 把一個 Index 的資料拆分成多個 Shard(分片),分散到不同的節點上。
Index: products (3 primary shards, 1 replica)
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Node 1 Node 2 Node 3 │
│ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ │
│ │ P0 │ │ P1 │ │ P2 │ │
│ │ (primary)│ │ (primary)│ │ (primary)│ │
│ ├──────────┤ ├──────────┤ ├──────────┤ │
│ │ R1 │ │ R2 │ │ R0 │ │
│ │ (replica)│ │ (replica)│ │ (replica)│ │
│ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
- Primary Shard:資料的原始分片。Index 建立後,Primary Shard 的數量不能更改(除非 reindex)。
- Replica Shard:Primary 的副本,提供讀取擴展和容錯。Replica 數量可以隨時調整。
- Shard 大小建議:每個 Shard 10-50GB。太小(1000 個 1MB 的 shard)浪費資源,太大(一個 500GB 的 shard)恢復慢。
- Over-sharding 是最常見的錯誤:很多人設定太多 shard(例如每個日期 index 都 5 個 shard),結果叢集有上萬個 shard,master node 管理開銷極大。一個小型應用,1-3 個 primary shard 就夠了。
# 建立 Index 時指定 shard 數量
curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/products" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}'Inverted Index(倒排索引)
Elasticsearch 之所以能做到毫秒級的全文搜尋,核心在於 Inverted Index。概念和書本的「索引頁」一樣——不是從頭到尾翻書找關鍵字,而是先查索引,直接翻到對應的頁碼。
假設有三筆文件:
| Doc ID | Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | ”Elasticsearch is fast” |
| 2 | ”PostgreSQL is reliable” |
| 3 | ”Elasticsearch is reliable and fast” |
Inverted Index 長這樣:
| Term | Document IDs |
|---|---|
| elasticsearch | [1, 3] |
| fast | [1, 3] |
| is | [1, 2, 3] |
| postgresql | [2] |
| reliable | [2, 3] |
| and | [3] |
搜尋 elasticsearch fast 時,查找 elasticsearch → [1, 3],查找 fast → [1, 3],取交集 → [1, 3]。不需要掃描每筆文件。
但這也解釋了為什麼 Elasticsearch 的更新(update)成本高:修改一筆文件意味著要更新所有相關 term 的 inverted index。實際上 Elasticsearch 不會就地更新(in-place update),而是把舊文件標記為刪除、寫入一筆新文件,然後在背景做 merge。
Mapping 設計
Mapping 是 Elasticsearch 的 Schema——定義每個欄位的型態、分析方式。Mapping 設計的好壞直接影響搜尋品質和效能。
基本 Mapping
一個電商產品的 Mapping 範例:
PUT /products
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 2,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard"
},
"title_keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"description": {
"type": "text"
},
"category": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"brand": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
},
"in_stock": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"created_at": {
"type": "date",
"format": "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis"
},
"tags": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"rating": {
"type": "float"
},
"sold_count": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}text vs keyword
這是 Mapping 設計中最核心的決策。搞混了就會出現「搜不到」或「效能很差」的問題。
| text | keyword | |
|---|---|---|
| 是否分詞(Analyzed) | 是(經過 Tokenizer 拆分、Token Filter 處理) | 否(完整儲存,不拆分) |
| 搜尋方式 | 全文搜尋(match query) | 精確匹配(term query)、篩選、排序、聚合 |
| 範例欄位 | 文章標題、文章內容、產品描述 | 分類名稱、Email、訂單狀態、標籤 |
| 佔用空間 | 較大(儲存 inverted index + 原始值) | 較小(只儲存原始值 + doc values) |
常見的錯誤:
// 錯誤:把 category 設為 text
"category": { "type": "text" }
// 用 term query 篩選 category = "Electronics"
{ "term": { "category": "Electronics" } }
// 結果:找不到!因為 text 欄位經過 analyzer 處理,
// "Electronics" 被轉成小寫 "electronics" 儲存,
// 而 term query 是精確匹配,不會做小寫轉換。// 正確:category 用 keyword 類型
"category": { "type": "keyword" }
// 或者用 term query 搜尋小寫值
{ "term": { "category": "electronics" } }Dynamic Mapping 的陷阱
如果你不定義 Mapping 就直接寫入資料,Elasticsearch 會自動偵測欄位類型(Dynamic Mapping)。聽起來很方便,但在 production 環境是個地雷:
- 字串自動偵測:所有字串都會被同時建立
text和keyword子欄位,浪費空間。 - 數字字串被偵測為 text:JSON 裡的
"price": "99.99"(字串)會被當成 text,無法做數值範圍查詢。 - 日期格式不一致:第一筆資料的
created_at如果是"2024-01-01",ES 偵測為 date。但如果第二筆是"yesterday",就會報錯。 - Mapping explosion:如果你的 JSON 文件有動態的 key(例如
{"user_123": {...}, "user_456": {...}}),每個 key 都會建立一個欄位,可能產生數萬個欄位,拖垮叢集。
建議:production 環境永遠使用明確的 Mapping,並且關閉 dynamic mapping 或設為 strict:
PUT /products
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"title": { "type": "text" },
"category": { "type": "keyword" },
"price": { "type": "float" }
}
}
}設為 "strict" 後,寫入未定義的欄位會直接報錯,而不是默默建立新欄位。
Multi-field Mapping
同一個欄位常常有多種搜尋需求。例如 title:
- 全文搜尋需要
text類型 - 排序和聚合需要
keyword類型 - 自動補全需要
edge_ngram分詞
Multi-field mapping 讓你一個欄位同時滿足多種需求:
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
},
"autocomplete": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "autocomplete_analyzer",
"search_analyzer": "standard"
}
}
}
}
}
}使用方式:
// 全文搜尋
{ "match": { "title": "wireless headphones" } }
// 精確排序
{ "sort": [{ "title.keyword": "asc" }] }
// 自動補全
{ "match": { "title.autocomplete": "wire" } }注意 autocomplete 子欄位用了不同的 search_analyzer。這是因為 index 時需要用 edge_ngram 產生 prefix token(w, wi, wir, wire…),但搜尋時應該用 standard analyzer 直接匹配,否則搜尋 wire 也會被拆成 w, wi, wir, wire,導致結果太多。
Analyzer 深入
Analyzer 決定了 text 欄位如何被分詞和處理。搜尋品質的好壞很大程度取決於 Analyzer 的選擇。
Analyzer 的三個階段
原始文字 → [Character Filter] → [Tokenizer] → [Token Filter] → Terms
- Character Filter:在分詞之前對原始文字做字元級別的處理(例如移除 HTML 標籤、將
&轉為and)。 - Tokenizer:把文字拆分成 Token(例如按空白分割、按語言規則分詞)。
- Token Filter:對每個 Token 做進一步處理(例如轉小寫、移除停用詞、詞幹提取 stemming)。
以 standard analyzer 為例:
輸入: "The Quick Brown Fox Jumps!"
Character Filter: (無)
Tokenizer (standard): ["The", "Quick", "Brown", "Fox", "Jumps"]
Token Filter (lowercase): ["the", "quick", "brown", "fox", "jumps"]
內建 Analyzer
| Analyzer | 說明 | 適用場景 |
|---|---|---|
standard | Unicode 分詞 + 小寫轉換 | 通用,大多數西方語言 |
simple | 按非字母字元分割 + 小寫 | 簡單的文字搜尋 |
whitespace | 只按空白分割,不做其他處理 | 需要保留大小寫和標點的場景 |
english | Standard + 英文停用詞 + 英文 stemming | 英文內容(running → run) |
keyword | 不做任何分詞,整個值作為一個 term | 不需要分詞但需要 text 功能時 |
Custom Analyzer 範例:自動補全
自動補全(Autocomplete)是搜尋引擎最常見的功能。使用者輸入幾個字,下拉選單即時顯示建議。實作方式是用 edge_ngram tokenizer:
PUT /products
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"autocomplete_analyzer": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "autocomplete_tokenizer",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
}
},
"tokenizer": {
"autocomplete_tokenizer": {
"type": "edge_ngram",
"min_gram": 2,
"max_gram": 10,
"token_chars": ["letter", "digit"]
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"fields": {
"autocomplete": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "autocomplete_analyzer",
"search_analyzer": "standard"
}
}
}
}
}
}edge_ngram 的效果:
輸入: "Headphones"
Tokens: ["He", "Hea", "Head", "Headp", "Headph", "Headpho", "Headphon", "Headphone", "Headphones"]
經過 lowercase: ["he", "hea", "head", "headp", "headph", "headpho", "headphon", "headphone", "headphones"]
所以當使用者輸入 head 時,就能匹配到 Headphones 這筆文件。
CJK(中日韓)搜尋
中文搜尋是個特殊的挑戰,因為中文沒有空格分隔詞彙。standard analyzer 對 CJK 字元的處理方式是 bigram(兩個字一組):
輸入: "全文搜尋引擎"
Standard analyzer tokens: ["全文", "文搜", "搜尋", "尋引", "引擎"]
Bigram 能用,但不夠精準。「搜尋引擎」應該是一個詞,被拆成「搜尋」「尋引」「引擎」三個 bigram,搜尋「引擎」會匹配到包含「引擎」這個 bigram 的所有文件,但也可能匹配到「引擎蓋」這類不相關的文字。
更好的做法是用中文分詞 plugin:
IK Analyzer(中文)
IK 是最常用的中文分詞 plugin,提供兩種模式:
ik_smart:粗粒度分詞(「中華人民共和國」→「中華人民共和國」)ik_max_word:細粒度分詞(「中華人民共和國」→「中華人民」「中華」「華人」「人民共和國」「人民」「共和國」「共和」「國」)
# 安裝 IK analyzer plugin(需要重啟 ES)
bin/elasticsearch-plugin install https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.12.0
# Docker 環境可以在 Dockerfile 中安裝
# FROM docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.12.0
# RUN bin/elasticsearch-plugin install https://get.infini.cloud/elasticsearch/analysis-ik/8.12.0PUT /articles
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"chinese_smart": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "ik_smart",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
},
"chinese_max": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "ik_max_word",
"filter": ["lowercase"]
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "chinese_max",
"search_analyzer": "chinese_smart"
},
"body": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "chinese_max",
"search_analyzer": "chinese_smart"
}
}
}
}Index 時用 ik_max_word(細粒度,產生更多 token,提高召回率),搜尋時用 ik_smart(粗粒度,使用者的查詢通常是完整的詞)。
Kuromoji(日文)
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"japanese": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "kuromoji_tokenizer",
"filter": ["kuromoji_baseform", "kuromoji_part_of_speech", "lowercase"]
}
}
}
}
}查詢(Query DSL)
Elasticsearch 的查詢語言叫 Query DSL,用 JSON 表達。看起來冗長,但結構清晰,而且可以組合出非常複雜的查詢邏輯。
Match Query(全文搜尋)
最基本的全文搜尋查詢:
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "wireless bluetooth headphones"
}
}
}match query 會先把搜尋字串用該欄位的 analyzer 分詞,然後搜尋包含任一 token 的文件。預設行為是 OR——包含 wireless、bluetooth、headphones 任何一個詞的文件都會匹配。
如果要求所有詞都要匹配:
{
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "wireless bluetooth headphones",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}模糊搜尋——處理拼字錯誤:
{
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "wireles headphnes",
"fuzziness": "AUTO"
}
}
}fuzziness: "AUTO" 根據搜尋字串長度自動決定允許的編輯距離(1-2 個字元的增刪改)。
Bool Query(組合查詢)
真實世界的搜尋通常需要組合多個條件。Bool query 是最常用的組合方式:
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "title": "headphones" } }
],
"filter": [
{ "term": { "category": "Electronics" } },
{ "range": { "price": { "gte": 50, "lte": 300 } } },
{ "term": { "in_stock": true } }
],
"should": [
{ "match": { "description": "noise cancelling" } },
{ "range": { "rating": { "gte": 4.5 } } }
],
"must_not": [
{ "term": { "brand": "CheapBrand" } }
],
"minimum_should_match": 1
}
}
}四個子句的差異:
| 子句 | 是否必須匹配 | 是否影響評分 | 是否使用快取 |
|---|---|---|---|
must | 是 | 是 | 否 |
filter | 是 | 否 | 是 |
should | 否(除非設定 minimum_should_match) | 是 | 否 |
must_not | 排除匹配的文件 | 否 | 是 |
must vs filter 的關鍵差異:兩者都要求匹配,但 filter 不計算評分(score),而且結果會被快取。所以:
- 需要影響搜尋結果排序的條件放
must(例如全文搜尋) - 只需要篩選、不需要評分的條件放
filter(例如分類、價格範圍、庫存狀態)
這不只是語意上的區別——效能差異很大。Filter context 的查詢結果會被 Elasticsearch 快取在 Node Query Cache 裡,同樣的篩選條件再次查詢時直接從快取返回。
Multi-match Query(多欄位搜尋)
使用者的搜尋字串應該同時搜尋標題、描述、標籤等多個欄位:
{
"multi_match": {
"query": "noise cancelling headphones",
"fields": ["title^3", "description", "tags^2"],
"type": "best_fields",
"fuzziness": "AUTO"
}
}title^3 表示標題的權重是 3 倍——標題匹配的文件會排在更前面。
type 的選項:
best_fields:取評分最高的欄位的分數(預設,適合大多數情況)most_fields:所有匹配欄位的分數加總(適合同一個內容被不同方式分詞的場景)cross_fields:跨欄位匹配(適合姓 + 名這種拆分在不同欄位的場景)
Aggregation(聚合 / 分面搜尋)
Aggregation 是 Elasticsearch 最強大的功能之一。不只是搜尋,還能同時做統計分析。電商的分面搜尋就靠它:
GET /products/_search
{
"size": 20,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [{ "match": { "title": "headphones" } }],
"filter": [{ "term": { "in_stock": true } }]
}
},
"aggs": {
"by_category": {
"terms": {
"field": "category",
"size": 20
}
},
"by_brand": {
"terms": {
"field": "brand",
"size": 20
}
},
"price_ranges": {
"range": {
"field": "price",
"ranges": [
{ "key": "budget", "to": 50 },
{ "key": "mid-range", "from": 50, "to": 200 },
{ "key": "premium", "from": 200, "to": 500 },
{ "key": "luxury", "from": 500 }
]
}
},
"avg_price": {
"avg": { "field": "price" }
},
"rating_stats": {
"stats": { "field": "rating" }
}
}
}回應會同時包含搜尋結果(hits)和聚合結果(aggregations):
{
"hits": { "total": { "value": 342 }, "hits": [...] },
"aggregations": {
"by_category": {
"buckets": [
{ "key": "Electronics", "doc_count": 210 },
{ "key": "Accessories", "doc_count": 132 }
]
},
"price_ranges": {
"buckets": [
{ "key": "budget", "doc_count": 45 },
{ "key": "mid-range", "doc_count": 180 },
{ "key": "premium", "doc_count": 95 },
{ "key": "luxury", "doc_count": 22 }
]
},
"avg_price": { "value": 156.78 },
"rating_stats": {
"count": 342, "min": 1.5, "max": 5.0,
"avg": 4.12, "sum": 1409.04
}
}
}這就是為什麼 Elasticsearch 的分面搜尋遠比 PostgreSQL 的 GROUP BY 強大——一次查詢同時返回搜尋結果和多維度的統計。
Function Score(自定義評分)
預設的相關性評分(BM25)只考慮文字匹配。但真實的搜尋排序還需要考慮其他因素:
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "headphones",
"fields": ["title^3", "description"]
}
},
"functions": [
{
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "sold_count",
"factor": 0.1,
"modifier": "log1p",
"missing": 1
},
"weight": 2
},
{
"gauss": {
"created_at": {
"origin": "now",
"scale": "30d",
"decay": 0.5
}
},
"weight": 1
},
{
"filter": { "range": { "rating": { "gte": 4.5 } } },
"weight": 1.5
}
],
"score_mode": "sum",
"boost_mode": "multiply"
}
}
}這個查詢的評分邏輯:
- 基礎分數:文字匹配的 BM25 分數
- 銷量加成:
log1p(sold_count * 0.1)× 權重 2(熱門商品排更前面) - 新鮮度加成:30 天內的商品分數較高,越舊衰減越多
- 高評分加成:評分 >= 4.5 的商品額外加 1.5 倍權重
效能調校
Elasticsearch 在小資料量下「什麼都不調就很快」,但資料量一大,不調校的話效能會急遽下降。
Index 層面的調校
1. Refresh Interval
Elasticsearch 寫入資料後,要經過 refresh 才能被搜尋到。預設 refresh interval 是 1 秒。這對應用搜尋來說通常 OK,但在大量批次匯入時應該調大:
// 批次匯入前:暫停 refresh
PUT /products/_settings
{ "index": { "refresh_interval": "-1" } }
// 批次匯入...(使用 _bulk API)
// 批次匯入後:恢復 refresh 並立即 refresh 一次
PUT /products/_settings
{ "index": { "refresh_interval": "1s" } }
POST /products/_refresh2. Bulk API
單筆寫入的效率極低。永遠使用 Bulk API 批次寫入:
POST /_bulk
{"index": {"_index": "products", "_id": "1"}}
{"title": "Wireless Headphones", "price": 99.99, "category": "Electronics"}
{"index": {"_index": "products", "_id": "2"}}
{"title": "USB-C Cable", "price": 12.99, "category": "Accessories"}
{"index": {"_index": "products", "_id": "3"}}
{"title": "Bluetooth Speaker", "price": 49.99, "category": "Electronics"}建議每批 1000-5000 筆文件,或每批 5-15MB。不要一次送太大的 bulk request(例如 100MB),會造成記憶體壓力。
3. 批次匯入時的 Replica 策略
匯入大量資料時,把 replica 設為 0,匯入完成後再恢復:
// 匯入前
PUT /products/_settings
{ "index": { "number_of_replicas": 0 } }
// 匯入完成後
PUT /products/_settings
{ "index": { "number_of_replicas": 1 } }這樣 primary shard 寫入時不需要同步到 replica,速度快很多。
Query 層面的調校
1. Filter 取代 Query
再次強調:不需要評分的條件放 filter,不要放 must。
// 慢:所有條件都在 must 裡,都要計算評分
{
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "title": "headphones" } },
{ "term": { "category": "Electronics" } },
{ "range": { "price": { "lte": 200 } } }
]
}
}
// 快:只有全文搜尋需要評分,其餘放 filter
{
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "title": "headphones" } }
],
"filter": [
{ "term": { "category": "Electronics" } },
{ "range": { "price": { "lte": 200 } } }
]
}
}2. 避免 Wildcard Query
// 極慢:需要掃描所有 term
{ "wildcard": { "title": "*phone*" } }
// 好得多:使用 match query,讓 analyzer 處理
{ "match": { "title": "phone" } }
// 如果需要 prefix 搜尋,用 prefix query 或 edge_ngram
{ "prefix": { "title.autocomplete": "phone" } }3. _source Filtering
如果你只需要文件的某些欄位(例如列表頁只需要標題和價格),不要返回整個 _source:
GET /products/_search
{
"_source": ["title", "price", "category", "rating"],
"query": { "match": { "title": "headphones" } }
}對大型文件(例如包含長文章內容的文件),這能顯著減少網路傳輸量。
4. Profile API
不確定查詢為什麼慢?用 Profile API 分析:
GET /products/_search
{
"profile": true,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [{ "match": { "title": "headphones" } }],
"filter": [{ "term": { "category": "Electronics" } }]
}
}
}回應會包含每個查詢階段的耗時,幫你找到瓶頸。
Cluster 層面的調校
1. JVM Heap 設定
Elasticsearch 跑在 JVM 上,heap 大小直接影響效能和穩定性。
- 設為 RAM 的 50%:剩下 50% 留給 OS 的 filesystem cache,Elasticsearch 靠它來快取磁碟上的 index 資料。
- 不超過 32GB:JVM 在 heap ⇐ 32GB 時使用 Compressed Ordinary Object Pointers(Compressed OOPs),記憶體使用效率更高。超過 32GB 反而可能比 31GB 更慢。
- Xms = Xmx:最小和最大 heap 設為一樣,避免 JVM 動態調整 heap 大小帶來的暫停。
# docker-compose.yml
environment:
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms4g -Xmx4g" # 8GB RAM 的機器| 機器 RAM | 建議 Heap | 留給 OS Cache |
|---|---|---|
| 8 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB |
| 16 GB | 8 GB | 8 GB |
| 32 GB | 16 GB | 16 GB |
| 64 GB | 31 GB | 33 GB |
2. Dedicated Master Nodes
小型叢集(1-3 節點)每個節點身兼 master、data、ingest 角色。但當叢集超過 5 個節點時,應該設定 3 個 dedicated master node(只做叢集管理,不存資料):
# master node
environment:
- node.roles=master
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms2g -Xmx2g"
# data node
environment:
- node.roles=data,ingest
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms16g -Xmx16g"3. Hot-Warm-Cold 架構
對時間序列資料(日誌、指標、時間相關的搜尋資料),用不同等級的硬體存放不同時期的資料:
- Hot nodes:SSD,最新的資料,高寫入/高查詢
- Warm nodes:HDD 或低階 SSD,較舊的資料,只讀查詢
- Cold nodes:HDD,最舊的資料,偶爾查詢
搭配 Index Lifecycle Management(ILM) 自動把 index 從 hot 搬到 warm、再搬到 cold:
PUT _ilm/policy/search-data-policy
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": {
"min_age": "0ms",
"actions": {
"rollover": {
"max_size": "30GB",
"max_age": "7d"
},
"set_priority": { "priority": 100 }
}
},
"warm": {
"min_age": "30d",
"actions": {
"shrink": { "number_of_shards": 1 },
"forcemerge": { "max_num_segments": 1 },
"set_priority": { "priority": 50 },
"allocate": {
"require": { "data": "warm" }
}
}
},
"cold": {
"min_age": "90d",
"actions": {
"set_priority": { "priority": 0 },
"allocate": {
"require": { "data": "cold" }
}
}
},
"delete": {
"min_age": "365d",
"actions": {
"delete": {}
}
}
}
}
}Docker Compose 開發環境範例
一個完整的本地開發環境,包含 Elasticsearch 和 Kibana:
# docker-compose.search.yml
services:
elasticsearch:
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.12.0
container_name: es-search
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- discovery.type=single-node
- xpack.security.enabled=false
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms4g -Xmx4g"
- cluster.name=search-cluster
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
ulimits:
memlock:
soft: -1
hard: -1
volumes:
- es-search-data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:9200:9200"
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "curl -fsSL http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health || exit 1"]
interval: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 10
kibana:
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:8.12.0
container_name: kibana-search
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://elasticsearch:9200
ports:
- "5601:5601"
depends_on:
elasticsearch:
condition: service_healthy
volumes:
es-search-data:# 啟動
docker compose -f docker-compose.search.yml up -d
# 確認健康狀態
curl -s http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health | python3 -m json.tool
# 查看節點資訊
curl -s http://localhost:9200/_cat/nodes?v
# 查看所有 index
curl -s http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?vPostgreSQL FTS vs Elasticsearch 決策
什麼時候用哪個?這是實務上最常被問到的問題。
| 考量面向 | PostgreSQL FTS | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|---|
| 建置成本 | 零(內建功能) | 需要獨立的叢集 |
| 維運成本 | 現有資料庫的一部分 | 額外的基礎設施 |
| 資料一致性 | ACID(強一致性) | Eventually consistent |
| 資料同步 | 不需要(資料在同一個 DB) | 需要建立同步管線 |
| 搜尋功能 | 基本到好 | 好到卓越 |
| 模糊搜尋 | 有限(pg_trgm 可做到但效能差) | 優秀(fuzziness 內建) |
| 分面搜尋 | 手動寫(慢) | 內建 Aggregation(快) |
| 自動補全 | 需要自己實作 | edge_ngram / completion |
| 中文搜尋 | 需要額外設定(zhparser) | IK analyzer plugin |
| 擴展性 | 單節點(read replica 有限幫助) | 水平擴展(加節點就好) |
| 適用資料量 | < 1000 萬筆 | 任何規模 |
| 最佳場景 | 搜尋是應用的輔助功能 | 搜尋是應用的核心功能 |
決策流程:
需要搜尋功能
├── 資料量 < 100 萬筆,搜尋需求簡單?
│ └── 用 PostgreSQL FTS(LIKE / tsvector + tsquery)
├── 資料量 100 萬 ~ 1000 萬筆,需要基本的全文搜尋?
│ └── 先試 PostgreSQL FTS + GIN Index
│ ├── 效能夠用?→ 維持 PostgreSQL FTS
│ └── 效能不夠?→ 引入 Elasticsearch
├── 需要模糊搜尋、自動補全、分面搜尋、複雜排序?
│ └── 直接用 Elasticsearch
└── 資料量 > 1000 萬筆?
└── 直接用 Elasticsearch
資料同步策略(PostgreSQL → Elasticsearch)
一旦決定同時使用 PostgreSQL(Primary Data Store)和 Elasticsearch(Search Engine),就面臨一個核心問題:怎麼讓兩邊的資料保持一致?
方式一:Application Dual-Write
應用在寫入 PostgreSQL 的同時,也寫入 Elasticsearch。
# Python pseudo-code
async def create_product(product_data):
# 1. 寫入 PostgreSQL
product = await db.products.create(product_data)
# 2. 寫入 Elasticsearch
await es.index(index="products", id=product.id, body={
"title": product.title,
"description": product.description,
"category": product.category,
"price": product.price,
})
return product優點:簡單直覺,延遲最低。
缺點:
- 如果 PostgreSQL 寫入成功但 ES 寫入失敗(ES 暫時不可用),資料就不一致了。
- 沒有 distributed transaction 來保證兩邊都成功或都失敗。
- 每個寫入資料的地方都要記得同時寫 ES,容易遺漏。
適用場景:小型應用,能接受偶爾的資料不一致。要搭配定期的全量同步來修正不一致。
方式二:CDC(Change Data Capture)with Debezium
監聽 PostgreSQL 的 WAL(Write-Ahead Log),自動將資料變更同步到 Elasticsearch。
PostgreSQL WAL → Debezium Connector → Kafka → Elasticsearch Sink Connector → ES
# Debezium PostgreSQL Source Connector 設定
{
"name": "pg-source",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.postgresql.PostgresConnector",
"database.hostname": "postgresql",
"database.port": "5432",
"database.user": "replicator",
"database.password": "secret",
"database.dbname": "myapp",
"table.include.list": "public.products,public.categories",
"topic.prefix": "myapp",
"plugin.name": "pgoutput",
"slot.name": "debezium_products"
}
}# Elasticsearch Sink Connector 設定
{
"name": "es-sink",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.confluent.connect.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchSinkConnector",
"connection.url": "http://elasticsearch:9200",
"topics": "myapp.public.products",
"key.ignore": "false",
"schema.ignore": "true",
"type.name": "_doc",
"transforms": "extractKey",
"transforms.extractKey.type": "org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.ExtractField$Key",
"transforms.extractKey.field": "id"
}
}優點:
- 資料變更自動同步,不需要修改應用程式碼。
- 基於 WAL,不會遺漏任何變更。
- 解耦應用和搜尋引擎。
缺點:
- 增加基礎設施複雜度(需要 Kafka + Debezium)。
- 有幾秒到幾十秒的同步延遲。
- 需要處理 schema 變更(PostgreSQL 加了新欄位,ES 的 mapping 也要更新)。
適用場景:中大型應用,需要可靠的資料同步,能接受幾秒的延遲。
方式三:Scheduled Batch Sync
定期(例如每 5 分鐘)從 PostgreSQL 查詢最近更新的資料,批次寫入 Elasticsearch。
# 定時任務(每 5 分鐘執行一次)
async def sync_products_to_es():
last_sync = await get_last_sync_timestamp()
# 查詢最近更新的產品
products = await db.execute(
"SELECT * FROM products WHERE updated_at > $1 ORDER BY updated_at",
last_sync
)
if not products:
return
# 批次寫入 Elasticsearch
bulk_body = []
for product in products:
bulk_body.append({"index": {"_index": "products", "_id": str(product.id)}})
bulk_body.append({
"title": product.title,
"description": product.description,
"category": product.category,
"price": float(product.price),
"updated_at": product.updated_at.isoformat(),
})
await es.bulk(body=bulk_body)
# 記錄同步時間
await set_last_sync_timestamp(products[-1].updated_at)優點:
- 實作簡單,不需要額外基礎設施。
- 批次寫入效率高。
缺點:
- 同步延遲較大(分鐘級)。
- 需要
updated_at欄位,且所有更新都要更新這個欄位。 - 刪除操作需要特殊處理(soft delete 或維護一個刪除記錄表)。
適用場景:搜尋資料不需要即時更新的場景(例如產品目錄,一天更新幾次就夠了)。
方式比較
| Dual-Write | CDC (Debezium) | Batch Sync | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 同步延遲 | 即時 | 秒級 | 分鐘級 |
| 資料一致性 | 低(可能失敗) | 高(基於 WAL) | 中(批次間有差距) |
| 實作複雜度 | 低 | 高(Kafka + Debezium) | 低 |
| 維運複雜度 | 低 | 高 | 低 |
| 對應用侵入性 | 高(每個寫入點都要改) | 零 | 低(只需定時任務) |
| 適用規模 | 小型 | 中大型 | 中型 |
建議:從 Batch Sync 開始。大多數應用的搜尋資料不需要即時同步(使用者不會注意到 5 分鐘的延遲)。等到業務需求明確需要即時搜尋(例如庫存搜尋、即時通訊搜尋),再升級到 CDC。
常見問題與風險
Mapping Explosion
如果你的 JSON 文件有動態的 key(例如使用者自定義的 metadata),每個 key 都會在 mapping 裡新增一個欄位。當欄位數量達到數萬時,叢集效能會急劇下降——每次寫入都要更新 cluster state,master node 忙不過來。
// 壞的做法:動態 key 作為欄位名
{
"product_id": "123",
"metadata": {
"color": "red",
"size": "L",
"custom_field_12345": "some value" // 每個產品不同的 key
}
}
// 好的做法:用嵌套的 key-value pair
{
"product_id": "123",
"metadata": [
{ "key": "color", "value": "red" },
{ "key": "size", "value": "L" },
{ "key": "custom_field_12345", "value": "some value" }
]
}並且設定欄位數量上限:
PUT /products/_settings
{
"index.mapping.total_fields.limit": 500
}Cluster Yellow / Red Status
- Green:所有 primary 和 replica shard 都正常分配。
- Yellow:所有 primary shard 正常,但有 replica shard 未分配。單節點叢集永遠是 yellow(因為 replica 不能和 primary 在同一個節點上),這是正常的。
- Red:有 primary shard 未分配。部分資料不可用,需要立即處理。
# 查看叢集狀態
curl -s http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
# 查看未分配的 shard
curl -s http://localhost:9200/_cat/shards?v&h=index,shard,prirep,state,unassigned.reason | grep UNASSIGNED
# 查看未分配的原因
curl -s http://localhost:9200/_cluster/allocation/explain?pretty常見的 Red 狀態原因:
- 磁碟空間不足(ES 預設在磁碟使用率 > 85% 時停止分配 shard)
- 節點掛了且沒有 replica
- 資料損壞
Memory Pressure(記憶體壓力)
JVM Heap 使用率持續 > 75% 是警訊,> 85% 會觸發頻繁的 GC(Garbage Collection),導致搜尋延遲飆高甚至節點失去回應。
常見的記憶體消耗大戶:
- 太多 shard:每個 shard 佔用固定的記憶體開銷,1000 個小 shard 比 10 個大 shard 消耗更多記憶體。
- Fielddata:對
text欄位做排序或聚合時,ES 會把整個欄位載入記憶體(fielddata)。這是非常耗記憶體的操作——應該用keyword子欄位做排序和聚合。 - 太大的 Aggregation:
termsaggregation 的size設太大(例如 100000),會消耗大量記憶體。 - Deep Pagination:
from: 100000, size: 10需要在每個 shard 上取 100010 筆文件然後合併排序。用search_after取代。
// 壞的做法:深度分頁
GET /products/_search
{
"from": 100000,
"size": 10,
"query": { "match_all": {} }
}
// 好的做法:用 search_after
GET /products/_search
{
"size": 10,
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{ "created_at": "desc" },
{ "_id": "asc" }
],
"search_after": ["2024-09-14T10:30:00Z", "abc123"]
}資料不同步
使用 Elasticsearch 作為搜尋引擎時,和 PostgreSQL 的資料不同步是無法完全避免的。處理策略:
- 接受短暫的不一致:大多數應用可以接受幾秒到幾分鐘的搜尋延遲。使用者透過搜尋找到的文件,點進去的詳情頁應該從 PostgreSQL 讀取最新資料。
- 定期全量同步:每天或每週跑一次全量同步,修正累積的不一致。
- 監控同步狀態:比較 PostgreSQL 和 Elasticsearch 的文件數量,差異太大時發告警。
# 比較文件數量
PG_COUNT=$(psql -t -c "SELECT count(*) FROM products")
ES_COUNT=$(curl -s "http://localhost:9200/products/_count" | jq '.count')
echo "PostgreSQL: $PG_COUNT, Elasticsearch: $ES_COUNT, Diff: $((PG_COUNT - ES_COUNT))"實戰:Node.js 應用整合 Elasticsearch
一個完整的 Node.js 範例,展示如何在實際應用中使用 Elasticsearch:
// search-service.ts
import { Client } from '@elastic/elasticsearch';
const esClient = new Client({
node: process.env.ELASTICSEARCH_URL || 'http://localhost:9200',
requestTimeout: 5000,
maxRetries: 3,
});
// 初始化 Index(應用啟動時執行一次)
async function initProductIndex() {
const indexExists = await esClient.indices.exists({ index: 'products' });
if (!indexExists) {
await esClient.indices.create({
index: 'products',
body: {
settings: {
number_of_shards: 2,
number_of_replicas: 1,
analysis: {
analyzer: {
autocomplete_analyzer: {
type: 'custom',
tokenizer: 'autocomplete_tokenizer',
filter: ['lowercase'],
},
},
tokenizer: {
autocomplete_tokenizer: {
type: 'edge_ngram',
min_gram: 2,
max_gram: 10,
token_chars: ['letter', 'digit'],
},
},
},
},
mappings: {
dynamic: 'strict',
properties: {
title: {
type: 'text',
fields: {
keyword: { type: 'keyword' },
autocomplete: {
type: 'text',
analyzer: 'autocomplete_analyzer',
search_analyzer: 'standard',
},
},
},
description: { type: 'text' },
category: { type: 'keyword' },
brand: { type: 'keyword' },
price: { type: 'float' },
rating: { type: 'float' },
sold_count: { type: 'integer' },
in_stock: { type: 'boolean' },
tags: { type: 'keyword' },
created_at: { type: 'date' },
updated_at: { type: 'date' },
},
},
},
});
}
}
// 搜尋產品(帶分面)
interface SearchParams {
query: string;
category?: string;
brand?: string;
minPrice?: number;
maxPrice?: number;
inStock?: boolean;
page?: number;
pageSize?: number;
sortBy?: 'relevance' | 'price_asc' | 'price_desc' | 'newest' | 'rating';
}
async function searchProducts(params: SearchParams) {
const {
query,
category,
brand,
minPrice,
maxPrice,
inStock,
page = 1,
pageSize = 20,
sortBy = 'relevance',
} = params;
const filters: any[] = [];
if (category) filters.push({ term: { category } });
if (brand) filters.push({ term: { brand } });
if (inStock !== undefined) filters.push({ term: { in_stock: inStock } });
if (minPrice || maxPrice) {
const range: any = {};
if (minPrice) range.gte = minPrice;
if (maxPrice) range.lte = maxPrice;
filters.push({ range: { price: range } });
}
const sortMap: Record<string, any[]> = {
relevance: [{ _score: 'desc' }],
price_asc: [{ price: 'asc' }],
price_desc: [{ price: 'desc' }],
newest: [{ created_at: 'desc' }],
rating: [{ rating: 'desc' }, { sold_count: 'desc' }],
};
const searchBody: any = {
from: (page - 1) * pageSize,
size: pageSize,
_source: ['title', 'category', 'brand', 'price', 'rating', 'in_stock', 'tags'],
query: {
bool: {
must: query
? [{
multi_match: {
query,
fields: ['title^3', 'description', 'tags^2'],
fuzziness: 'AUTO',
},
}]
: [{ match_all: {} }],
filter: filters,
},
},
sort: sortMap[sortBy] || sortMap.relevance,
aggs: {
categories: { terms: { field: 'category', size: 30 } },
brands: { terms: { field: 'brand', size: 30 } },
price_ranges: {
range: {
field: 'price',
ranges: [
{ key: 'Under $50', to: 50 },
{ key: '$50-$100', from: 50, to: 100 },
{ key: '$100-$300', from: 100, to: 300 },
{ key: '$300+', from: 300 },
],
},
},
avg_rating: { avg: { field: 'rating' } },
},
};
const result = await esClient.search({
index: 'products',
body: searchBody,
});
return {
total: (result.hits.total as any).value,
products: result.hits.hits.map((hit: any) => ({
id: hit._id,
score: hit._score,
...hit._source,
})),
facets: {
categories: (result.aggregations?.categories as any)?.buckets || [],
brands: (result.aggregations?.brands as any)?.buckets || [],
priceRanges: (result.aggregations?.price_ranges as any)?.buckets || [],
avgRating: (result.aggregations?.avg_rating as any)?.value,
},
};
}
// 自動補全
async function autocomplete(prefix: string, limit = 5) {
const result = await esClient.search({
index: 'products',
body: {
size: limit,
_source: ['title', 'category'],
query: {
match: {
'title.autocomplete': {
query: prefix,
operator: 'and',
},
},
},
},
});
return result.hits.hits.map((hit: any) => ({
id: hit._id,
title: hit._source.title,
category: hit._source.category,
}));
}
export { initProductIndex, searchProducts, autocomplete };延伸閱讀
- ELK) — 日誌用途的 Elasticsearch
- 資料庫全景 — 選型指南
- PostgreSQL 進階 — PostgreSQL FTS