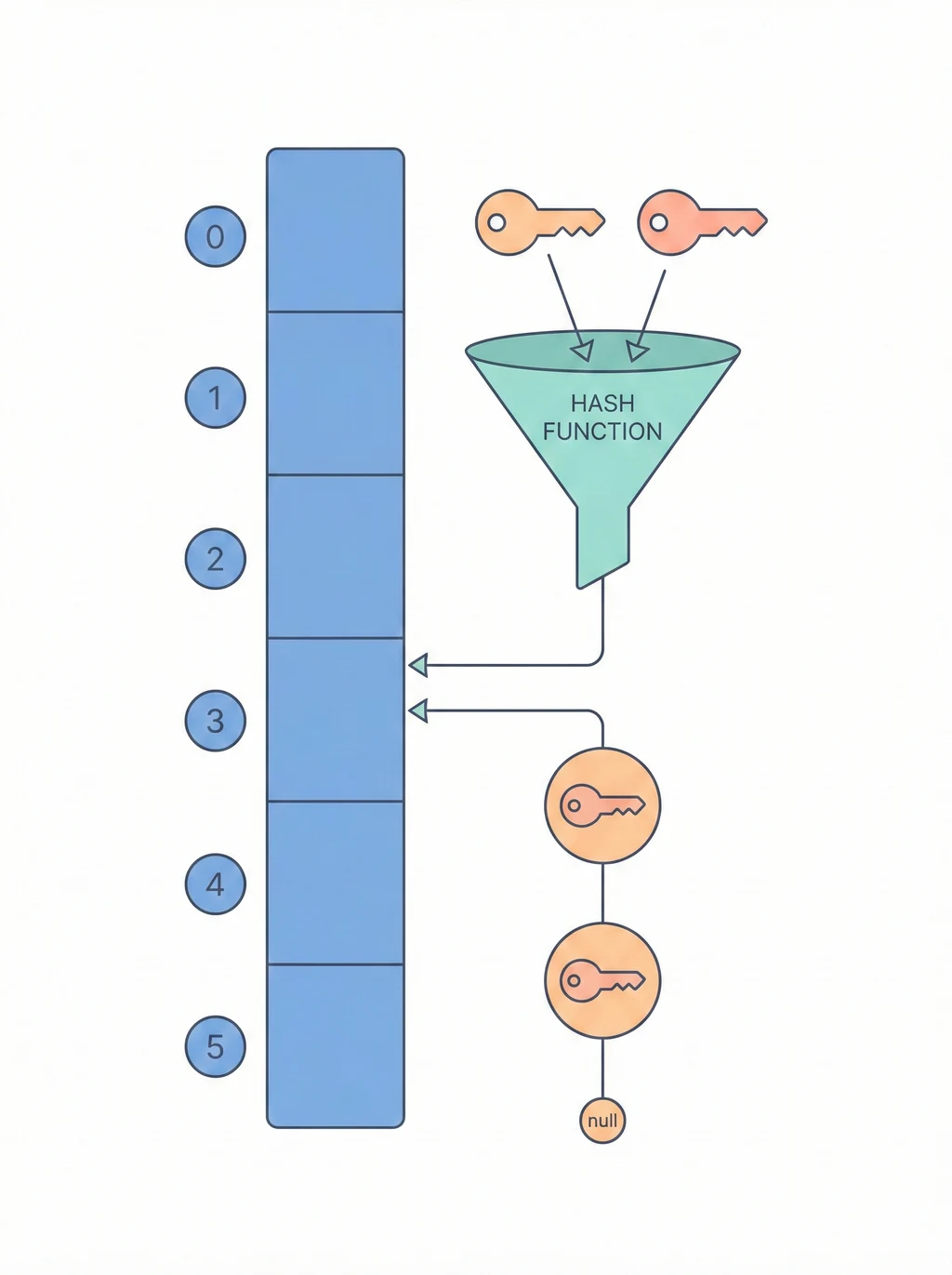
視覺化概覽
graph LR K1["key: apple"] -->|"hash()"| H["Hash Function"] K2["key: banana"] -->|"hash()"| H K3["key: grape"] -->|"hash()"| H H -->|"index 2"| B2 H -->|"index 1"| B1 H -->|"index 2"| B2 subgraph Buckets B0["[0] 空"] B1["[1] banana=200"] B2["[2] apple=100 → grape=400"] B3["[3] 空"] end style B2 fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px style H fill:#ff9,stroke:#333
你每天都在用 Hash Table
你寫過 const cache = {} 嗎?用過 new Map() 嗎?在 Redis 裡存過 session 嗎?這些全都是 hash table。
URL routing(Express 的 app.get('/users/:id'))、database indexing(MySQL 的 hash index)、session storage(Redis 的 key-value store)、甚至瀏覽器的 DNS cache,底層全是 hash table。它是你最常用、但可能最少深入理解的資料結構。
什麼是雜湊表?
雜湊表用 hash function 把 key 轉換成陣列 index,實現超快的查找。
key "apple" → hash("apple") → 3 → buckets[3] = 100
buckets:
[0]: null
[1]: null
[2]: null
[3]: "apple" = 100 ← 直接跳到這裡!
為什麼快?
| 操作 | Array | Linked List | Hash Table |
|---|---|---|---|
| 查找 | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) 平均 |
| 插入 | O(n) | O(1) 頭部 | O(1) 平均 |
| 刪除 | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) 平均 |
不用遍歷,直接算出位置!
Hash Function
把任意 key 轉成固定範圍的數字:
hash("apple") = 某個數字
index = hash("apple") % capacity
好的 hash function:
- 計算快
- 分布均勻(減少碰撞)
- 相同 key 永遠得到相同結果
碰撞 (Collision)
不同的 key 算出相同的 index:
hash("apple") % 4 = 2
hash("grape") % 4 = 2 ← 碰撞!
解法 1:分離鏈接法 (Separate Chaining)
每個 bucket 用 Linked List 存多個元素:
[0]: null
[1]: "banana"=200
[2]: "apple"=100 -> "grape"=400 ← 鏈起來
[3]: "cherry"=300
解法 2:開放定址法 (Open Addressing)
碰撞時找下一個空位:
hash("apple") = 2 → buckets[2] = "apple"
hash("grape") = 2 → 碰撞!往後找 → buckets[3] = "grape"
負載因子 (Load Factor)
負載因子 = 元素數量 / 桶數量
- 太高(> 0.75):碰撞多,變慢
- 太低:浪費空間
解法: 超過閾值就擴容(通常 2 倍),重新 hash 所有元素。
操作圖解
Put 操作
put("apple", 100):
1. hash("apple") % 4 = 2
2. buckets[2] = Entry("apple", 100)
[0]: null
[1]: null
[2]: "apple"=100 ← 放這裡
[3]: null
Get 操作
get("apple"):
1. hash("apple") % 4 = 2
2. 去 buckets[2] 找 key="apple"
3. 回傳 100
碰撞時的查找
buckets[2]: "apple"=100 -> "grape"=400
get("grape"):
1. hash("grape") % 4 = 2
2. buckets[2] 是 "apple",不對
3. 往後找 -> 找到 "grape"
4. 回傳 400
時間複雜度
| 操作 | 平均 | 最差 |
|---|---|---|
| put | O(1) | O(n) |
| get | O(1) | O(n) |
| remove | O(1) | O(n) |
最差情況:所有 key 都碰撞到同一個 bucket(變成 Linked List)。
經典應用
1. 字典/映射
Map<String, Integer> ages = new HashMap<>();
ages.put("Alice", 25);
ages.get("Alice"); // 252. 快取 (Cache)
Map<URL, Response> cache = new HashMap<>();
// 查過的網頁存起來,下次直接用3. 去重
Set<Integer> seen = new HashSet<>();
// 自動去除重複元素4. 統計頻率
Map<Character, Integer> freq = new HashMap<>();
for (char c : text.toCharArray()) {
freq.put(c, freq.getOrDefault(c, 0) + 1);
}JavaScript / TypeScript 實務:Map vs Object vs WeakMap
在 JS 裡你有三種 hash table 選擇,很多人搞混它們的用途:
| 特性 | Object {} | Map | WeakMap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key 類型 | 只能是 string/symbol | 任意值(object、number…) | 只能是 object |
| 順序 | 不保證(數字 key 會被排序) | 保證插入順序 | 不保證 |
| 大小 | 要自己算 Object.keys().length | .size 屬性 | 無法取得 |
| 效能 | 少量 key 較快 | 大量 key 較快(頻繁增刪) | 同 Map |
| GC | key 不會被回收 | key 不會被回收 | key 可被 GC 回收 |
什麼時候用什麼
// 1. 設定檔 / 結構固定 → 用 Object
const config = { port: 3000, host: 'localhost' };
// 2. 動態的 key-value / 需要頻繁增刪 → 用 Map
const sessions = new Map<string, { userId: string; expiry: number }>();
sessions.set('abc123', { userId: 'u001', expiry: Date.now() + 3600_000 });
sessions.delete('abc123');
console.log(sessions.size); // 0
// 3. 需要掛 metadata 在物件上,但不想阻止 GC → 用 WeakMap
const domCache = new WeakMap<HTMLElement, { width: number; height: number }>();
const el = document.getElementById('app')!;
domCache.set(el, { width: 100, height: 200 });
// 當 el 被從 DOM 移除且無其他引用時,WeakMap 裡的 entry 自動被回收實作:簡易 LRU Cache
LRU(Least Recently Used)Cache 是 hash table 最經典的工程應用。利用 Map 的插入順序保證,只需要不到 20 行就能實作:
class LRUCache<K, V> {
private cache = new Map<K, V>();
constructor(private capacity: number) {}
get(key: K): V | undefined {
if (!this.cache.has(key)) return undefined;
// 存取時移到最後面(最近使用)
const value = this.cache.get(key)!;
this.cache.delete(key);
this.cache.set(key, value);
return value;
}
put(key: K, value: V): void {
if (this.cache.has(key)) this.cache.delete(key);
this.cache.set(key, value);
// 超過容量就刪最舊的(Map 的第一個 entry)
if (this.cache.size > this.capacity) {
const oldest = this.cache.keys().next().value!;
this.cache.delete(oldest);
}
}
}
// 使用:API response cache,最多存 100 筆
const apiCache = new LRUCache<string, any>(100);
apiCache.put('/api/users/1', { name: 'Terry' });
apiCache.get('/api/users/1'); // { name: 'Terry' },同時標記為「最近使用」工程場景:瀏覽器的 HTTP cache、CDN 的 edge cache、ORM 的 query cache,底層都是 LRU 策略 + hash table。
安全議題:Hash Flooding 攻擊
Hash table 有一個鮮為人知的安全風險:攻擊者可以故意構造大量會碰撞到同一個 bucket 的 key,讓 O(1) 退化成 O(n),造成 DoS。
正常:100 萬個 key 均勻分布 → 查找 O(1)
攻擊:100 萬個 key 全碰撞到 bucket[0] → 查找 O(n) → CPU 100%
Node.js 的應對:
- V8 引擎使用隨機化的 hash seed,每次啟動不同
- Express 的
body-parser預設限制 JSON body 的 key 數量 - 你該做的:永遠限制使用者輸入的 key 數量,不要用 user input 當 Object key
什麼時候不需要 Hash Table
- 資料量很小(< 10 個 key):直接用 array linear search 就好,hash 的 overhead 反而更大
- 需要排序/範圍查詢:hash table 沒有順序概念,改用 Tree 或 sorted array
- 需要持久化:hash table 在記憶體中,持久化考慮 Trie(字串場景)或資料庫 index
延伸閱讀
- Tree 樹 — 需要排序的 key-value 選 BST
- Trie 前綴樹 — 字串搜尋的特化 hash 結構
- LRU Cache — Hash Table + Doubly Linked List 的經典組合
- 字串演算法 — 常用 hash 做 pattern matching(Rabin-Karp)
相關檔案
- Java 實作:HashTable.java
- 視覺化:hash-table.html